Date: June 16, 2025
Uneven brightness, color fading, or flickering at the far end of your LED strip? You're likely dealing with voltage drop. This post covers how to design long LED strip runs correctly using dual feeds, segment rules, higher voltages, and smart mounting strategies.
🔋 What Is Voltage Drop?
Voltage drop happens when power diminishes along the length of wire due to resistance. The longer the wire or the higher the current, the more voltage is lost — which means the LEDs at the end of the strip will receive less power than those at the beginning.
To maintain consistent light output, aim to keep voltage drop under 3%. Check out our voltage drop charts to calculate the proper wire size for your run.
📏 Max Recommended Segment Lengths
- 24V LED Strip: Up to 8m (26ft) per feed
- Narrow 24V Strip: Limit to 3m (10ft)
- 12V LED Strip: Typically 3–5m max
Always check the manufacturer’s spec sheet to confirm maximum current and trace size.
⚡ Try This Instead: 48V LED Strip
For longer runs with lower current draw, consider upgrading to 48V LED strip lighting. These run at half the current of 24V systems for the same wattage, significantly reducing voltage drop over distance.
- Ideal for large spaces or commercial installs
- Compatible with many 48V constant voltage power supplies
- Reduced heat and copper loss
🔁 When to Use Dual-End Feeds
If your strip run is approaching or exceeding the recommended max length, power it from both ends using a dual-feed setup:
- Connect both ends of the LED strip to the same power supply
- Use consistent polarity: + to + and - to -
- Use appropriate gauge wire for both feeds
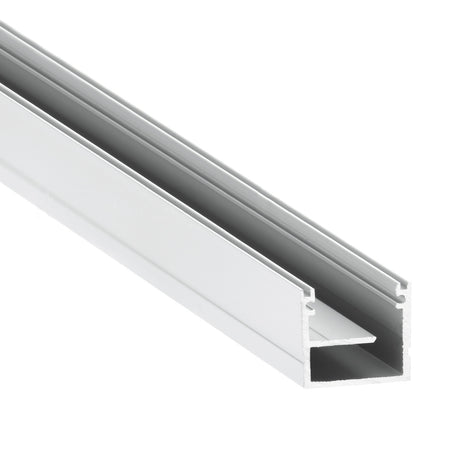
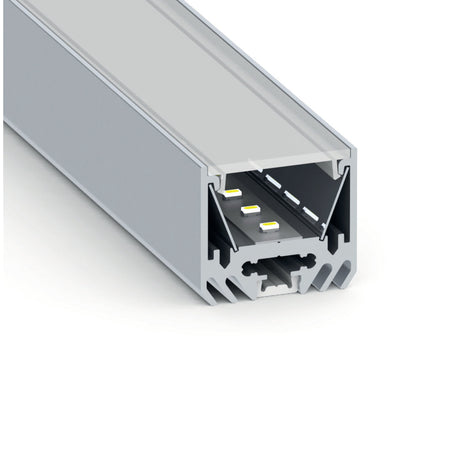
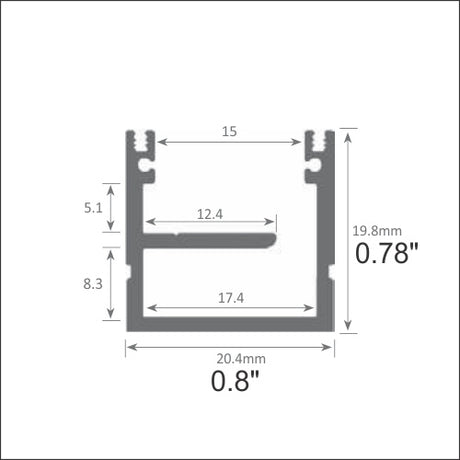
📦 Product Highlight: Versalles LED Channel with Raceway
Running long LED strips? The Versalles LED profile features an integrated wire conduit — making dual-feed or long cable routing clean and safe.

- IP65 surface-mount profile for indoor or outdoor use
- Concealed cable channel alongside LED strip
- Perfect for dual-feeds or long power feeds
- Clean install, reduced clutter, better airflow
⚠️ What Happens If You Don’t?
- Dim or discolored LED output at the far end
- LED lifespan is reduced due to overdriven traces
- Possible overheating of the strip or power supply
🔧 Segment Splitting Tips
If dual-feeding isn’t practical, break your strip into smaller segments and feed each individually:
- Use LED amplifiers for signal extension
- Bring the power supply closer to center of run
- Use heavier-gauge wire (e.g., 14AWG or 12AWG)
🔗 Related Resources
- Part 6: Wiring LED Strips Correctly
- Wire Size & Voltage Drop Charts
- 48V LED Strip Collection
- Wiring Accessories
✅ Best Practices Recap
- Respect the 3% voltage drop rule
- Stick to max strip segment lengths
- Use dual feeds or amplifiers when needed
- Upgrade to 48V for longer runs
- Use wire-rated LED profiles like the Versalles channel
📘 Up Next
Part 8: Troubleshooting, Testing, and Real-World LED Install Tips – Coming Soon!